A new study, partially funded by NCCOS, developed a framework for evaluating the physical, economic, and demographic impacts and benefits of engineered, nature-based, and hybrid adaptation strategies to address coastal flooding. The research team applied the framework to two neighboring communities on Santa Monica Bay in Los Angeles County, California, to illustrate its utility for local-scale planning (Figure 1).
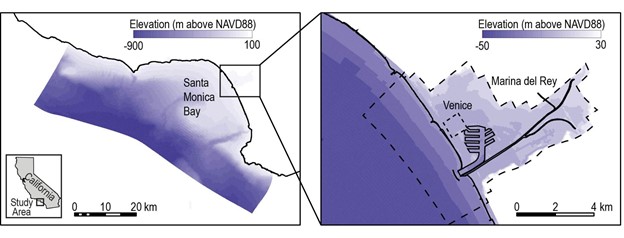
Across Los Angeles County, 60,000 residents and $22 billion in property are at risk of flooding due to sea level rise and storms over the next century, assuming no interventions. This integrated modeling approach allows communities to look at flooding to characterize the distribution of costs and benefits associated with different adaptation actions.
To investigate how the “gray” (e.g., seawalls, bulkheads) and nature-based shoreline adaptation approaches influence coastal flooding, the research team used CoSMoS, a physics-based numerical model developed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). CoSMoS can assess coastal flooding exposure as a result of tides, surge, and waves for various sea level rise and storm scenarios. To estimate economic and demographic impacts, the team applied and advanced the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s (FEMA) Hazus framework to assess their CoSMoS scenarios. Hazus is a standardized approach that allows hazard mitigation planners to assess the risk of different disasters.
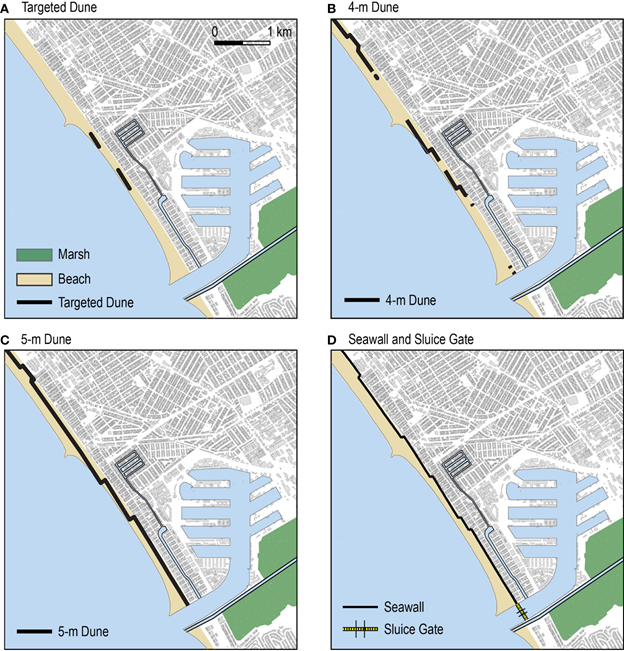
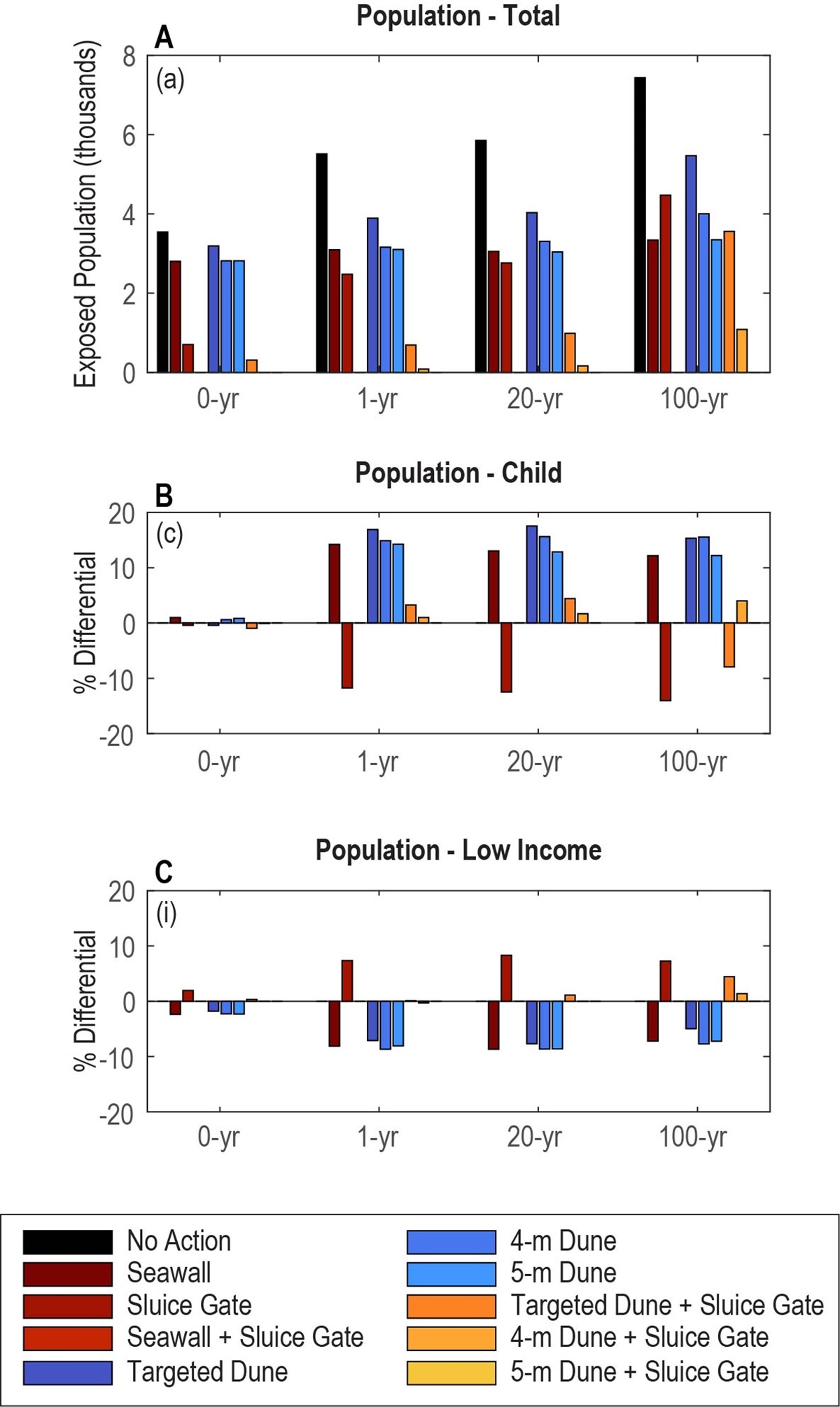
The team evaluated a range of engineered, nature-based, and hybrid adaptation strategies for a portion of Santa Monica Bay, California (Figure 2). Based on input from local workshops, the performance of nine stakeholder-prioritized coastal adaptation strategies were considered. Overall, dual approaches that provide protection along beaches using dunes or seawalls, and along inlets using sluice gates, perform best at reducing or eliminating flooding, damages, and population impacts. Adaptation strategies that include only a sluice gate and partial or no protection along the beach are effective at reducing flooding around the more affluent harbor area, but exacerbate flooding elsewhere, leading to unintended impacts on vulnerable populations (Figure 3). Overall the natural aspects of the mitigation actions considered in this study remain more in the “gray” realm in this example. However, there is great potential in the future where space and conditions allow for integrating more natural examples of flood mitigation within the developed framework.
This project is part of NCCOS’s Effects of Sea Level Rise (ESLR) Program; find out more about the project here. The project is co-led by Kevin Befus (University of Arkansas) and Michelle Hummel (University of Texas at Arlington).
Citation: Schroder, K., M.A. Hummel, K.M. Befus, P.L. Barnard. An integrated approach for physical, economic, and demographic evaluation of coastal flood hazard adaptation in Santa Monica Bay, California. Front. Mar Sci (9). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.1052373.
